Vincent Coll, Dougherty A, Hyatt M and Mayers N
DOI: 10.4172/1736-4337.1000266
We investigate properties of a Type-A meander, here considered to be a certain planar graph associated to seaweed subalgebra of the special linear Lie algebra. Meanders are designed in such a way that the index of the seaweed may be computed by counting the number and type of connected components of the meander. Specifically, the simplicial homotopy types of Type-A meanders are determined in the cases where there exist linear greatest common divisor index formulas for the associate seaweed. For Type-A seaweeds, the homotopy type of the algebra, defined as the homotopy type of its associated meander, is recognized as a conjugation invariant which is more granular than the Lie algebra's index.
DOI: 10.4172/1736-4337.1000267
By using the Jiang’s function J2 (ω) we prove that there exist infinitely many integers n such that n=2P1, n+1=3P2, n+k−1=(k+1) Pk are all composites for arbitrarily long k, where P1, P2,…, Pk are all primes. This result has no prior occurrence in the history of number theory.
DOI: 10.4172/1736-4337.1000268
Properties of fuzzy subalgebras and ideals of n-ary Lie algebras are described. Methods of construction fuzzy ideals are presented. Connections with various fuzzy quotient n-Lie algebras are proved.
DOI: 10.4172/1736-4337.1000269
Let Vect(ïÂ’ïÂÂ1) be the Lie algebra of smooth vector fields on ïÂ’ïÂÂ1. In this paper, we classify aff(1) -invariant linear differential operators from Vect(ïÂ’ïÂÂ1) to ï„λ,μ;v vanishing on aff(1), where ï„λ,μ;v≔Homdiff(ï†λ⊗ï†μ;ï†v) is the space of bilinear differential operators acting on weighted densities. This result allows us to compute the first differential aff(1)-relative cohomology of Vect(ïÂ’ïÂÂ1) with coefficients in ï„λ,μ;v
DOI: 10.4172/1736-4337.1000270
In this paper we show a few outcomes concerning two remaining deductions on a semi-prime ring are displayed. These outcomes are identified with an outcome which is motivated by Posner's hypothesis. This outcome affirms that if R is a 2-torsion free semi-prime ring, δ and g are non-zero remaining inductions of R with the end goal that g is a surjective on R, and g(y)δ(x)=g(x)δ(y) for all x,y∈R. At that point δ g can't be a non-zero left derivation. A thought of orthogonal left derivations emerges here.
Barna IF, Pocsai MA and Mátyás L
DOI: 10.4172/1736-4337.1000271
We present analytic self-similar solutions for the one, two and three dimensional Madelung hydrodynamical equation for a free particle. There is a direct connection between the zeros of the Madelung fluid density and the magnitude of the quantum potential.
DOI: 10.4172/1736-4337.1000272
The wavelets are important functions in the harmonic analysis. Up to our knowledge, apply wavelets to solve differential equations are limited to ODEs or PDEs with approximate and numerical solutions. In this paper, the novel methods based on the wavelets with two independent variables according to differential invariants are proposed. In fact, the transform groups are constructed that can be acted on the existing solutions and produced the new solution. These groups are based on the symmetry groups (obtained by the Lie symmetry method and other equivalence methods) and mother wavelets. The new method based on the wavelets are presented, new mother wavelets are produced, the corresponding wavelet type transform groups are provided and applied for solving the differential equations. Our method can be used for ODEs and PDEs at every order and give us the analytic solutions according to the existing solutions (from every method without any exception).
Akyar B and Kara Hansen A
DOI: 10.4172/1736-4337.1000273
In this work, we apply soft theory to control theory. With the inspiration of soft theory we define soft Lie groups and construct soft control systems on Lie groups with observation. For the decision argument, we use some observability characterization and give an example.
DOI: 10.4172/1736-4337.1000274
The main feature of the flame kinematics can be described with the G-equation. We investigate the solutions of the G-equation with the well-known self-similar Ansatz. The results are discussed and the method how to get selfsimilar solutions is briefly mentioned.
DOI: 10.4172/1736-4337.1000275
Let D be a mapping from an alternative ring 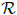 into itself satisfying D(a⋅ba)= D(a)⋅ba+a⋅D(b)a+a⋅bD(a) for all a, b
into itself satisfying D(a⋅ba)= D(a)⋅ba+a⋅D(b)a+a⋅bD(a) for all a, b 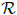 . Under some conditions on
. Under some conditions on 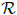 , we show that D is additive.
, we show that D is additive.
DOI: 10.4172/1736-4337.1000276
DOI: 10.4172/1736-4337.1000277
A new numerical method based on the approximation of polynomials is here proposed for solving the one dimensional parabolic partial differential equation arising from unsteady state flow of heat subject to initial and boundary conditions. The method results from discretization of the parabolic partial differential equation which leads to the production of a system of algebraic equations. By solving the system of algebraic equations we obtain the problem approximate solutions.
DOI: 10.4172/1736-4337.1000278
We classify, up to isomorphism, the 2-dimensional algebras over a field ï‹. We focuse also on the case of characteristic 2, identifying the matrices of GL(2, ï†2) with the elements of the symmetric group Σ3. The classification is then given by the study of the orbits of this group on a 3-dimensional plane, viewed as a Fano plane. As applications, we establish classifications of Jordan algebras, algebras of Lie type or Hom-Associative algebras.
DOI: 10.4172/1736-4337.1000279
The concept of moving space-matter of New Cartesian physics, based on the identity of space and matter, offers a way to materialist explanations of the paranormal and supernatural phenomena. It moves space-matter forms not only those objects and phenomena that are realized by our consciousness, but also those that escape his attention.
DOI: 10.4172/1736-4337.1000280
Santilli’s prime chains: Pj + 1=aPj ± b , j=1,⋯,k−1, (a,b)=1, 2|ab. If a −1 = P1λn Pnλn , P1⋯Pn|b, we have J2(ω)→∞ as ω→∞. There exist infinitely many primes P1 such that P2,⋯, Pk are primes for arbitrary length k. It is the Book proof. This is a generalized Euclid-Euler proof for the existence of infinitely many primes. Therefore Euclid-Euler-Jiang theorem in the distribution of primes is advanced. It is the Book theorem.