Hypothesis - (2021) Volume 10, Issue 3
Received: 29-Jan-2021
Published:
29-Mar-2021
, DOI: 10.37421/2169-0316.2021.10.286
Citation: Anand Sunder and Ibrahim Raji. "LP Modelling Framework to Evaluate Lean Implementation Effectiveness." Ind Eng Manage 10 (2021): 286.
Copyright: © 2021 Sunder A, et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
We propose a LP modeling approach for 7 types of lean waste, with effects of sub system improvements, including the effects of interdependence of type of waste effects on one another and objective function modeling for optimization and simulation of environmental waste is seen from [1,2]. Khalil [3] extensively explores a weighted measurement criterion between different types of wastes, this however isgood for a high level assessment of lean effectiveness. Tascione V [3], E.Solano [1]. However have bridged the gap by showing a wholistic modelling approach for minimizing waste at a case study level. We formulate our multi objective minimization LP Model as follows:
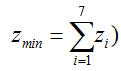 (Where
(Where
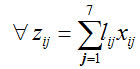
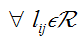 defined as the cost per unit waste type)
defined as the cost per unit waste type)
s.t,
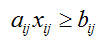 OR
OR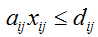
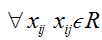 and
and 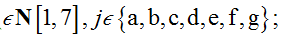
Interdependence effects of lean waste types on one another will require models to be built, we plan to evaluate and simulate the actual waste reduction achieved, against the optimum for given systems. A total of 7c2 or 21 interactions need to be evaluated.
Production Planning and Control • Capacity Planning • Master Production scheduling • Aggregate Production Planning • Demand Forecasting
Basing on a similar formulation approach used by Tascione V [3], E. Solano et al. [1], our benchmarking assumption defines an ideal lean system, as one where all waste types are independent of each other ∀xi (amount of waste).
Lean waste for each type i, is such that there are upper and lower bounds for waste resulted, this is determined by the system in question or scope for lean improvement.
Matrix formulation of the assumption:
AX ≥ D …….. (1) (Lower limit for waste)
AX ≤ B -------- (2) (upper limit on waste)
The minimum waste or cost function, can either be realized from a top-down approach (reducing actual waste, by running iterations of lean initiatives) or by bottom-up approach, iterative improvement of simulation models.
Here, in the simulation models too we assume that systems are such that all 7 types of lean wastes generated are independent of each other.
Assumptions for the Linear Programming model for minimizing waste:
Matrix formulation of the optimization problem
We assume here that waste matrix X has upper lower bounds
Min zobj = CX
AX ≤ B ……. (1)
AX ≥ D …….. (2)
X + S = B
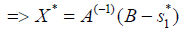
AX − S2 = D
Atoptimum
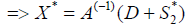
We arrive thus at an optimum, mathematically bidirectional [4].

Interaction affects between waste types, would have an effect on the optimum, as shown 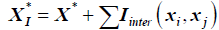 , where in regression modeling must be usedbased on collected data to model
, where in regression modeling must be usedbased on collected data to model 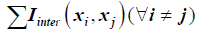
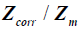 , measuring the corrected optimum versus ideal.
, measuring the corrected optimum versus ideal.
Data gathering on various lean implementation drives must be taken in and validated.
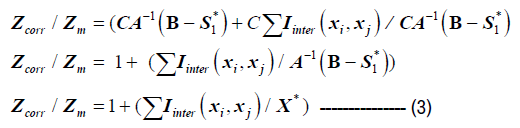
Conclusion or Proposed future study
Corrected optimum with interaction effects
From (3) we have 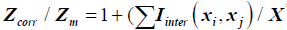 .
.
Where Zcorr is the corrected optimum due to interaction effects between different types of lean wastes, in the system of question
Zm Is the minimum for an ideal lean system
Interaction of lean waste types is modeled as shown below
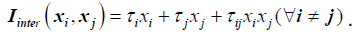
Khalil [2] et.al, explores a weighted measurement criterion, and similarly we define 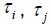 and
and 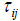 as adjustable weights.
as adjustable weights.
Curve fitting for 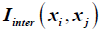 is proposed to de done using DOE.
is proposed to de done using DOE.
Industrial Engineering & Management received 739 citations as per Google Scholar report