Research Article - (2025) Volume 14, Issue 1
Received: 05-Jul-2024, Manuscript No. JACM-24-140881;
Editor assigned: 07-Jul-2024, Pre QC No. JACM-24-140881 (PQ);
Reviewed: 21-Jul-2024, QC No. JACM-24-140881;
Revised: 06-Feb-2025, Manuscript No. JACM-24-140881 (R);
Published:
13-Feb-2025
, DOI: 10.37421/2168-9679.2025.14.599
Citation: Naime, Jannatul, Muhammad Hanif and A N M Rezaul Karim. "Security System through Matrices in Cryptography." J Appl Computat Math 14 (2025): 599
Copyright: © 2025 Naime J, et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the creative commons attribution license which permits unrestricted use, distribution and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Communication over the internet must be secure to prevent intercepting or accessing sensitive information. Attempts are being made to protect confidential information by providing maximum security over the network. One of such techniques is using matrix multiplication for Hill Cipher cryptosystem, which is not easily breakable. The traditional Hill Cipher algorithm uses 2 × 2 and 3 × 3 matrix for generating keys. In this paper, we enhance the existing algorithm by using 4 × 4 matrix to generate the keys and to demonstrate the application of this algorithm created in MATLAB programming language. We also compare the time consumed to encode and decode the message by the traditional Hill Cipher algorithm. The enhanced Hill Cipher algorithm to get a clear idea which algorithm is more efficient and reliable and not easily breakable by the intruders.
2D and 3D matrix transformations • Hill Cipher algorithm • Cryptography • MATLAB programming
A significant quantity of digital data is exchanged across insecure routes today. Hacking is always a possibility when sharing private and confidential photographs over an open network. Researchers now have the difficult task of creating appropriate encryption methods to thwart various cryptanalytic attacks [1]. A tool for ensuring message confidentiality is cryptography. The phrase "composing mystery" has a unique connotation in Greek [2]. In plaintext, the working cycle that modifies the actual message is referred to as cypher text. The scrambling conversation loop recovers the chip text's original plaintext. Cryptography [3], which may be regarded as an ancient technology that has been used up to this point, ensures that the data supplied are protected with the ultimate goal of assuring the receiver can access this information from registered roots. Models date to 2000 BCE, when ''hidden'' hieroglyphic hieroglyphs were utilized by the extinct Egyptians, much as other evidence of the Caesar Code or Riddle creation in ancient Rome. Cryptography is regularly used by billions of people throughout the world to safeguard information and data, but most of them are unaware that they are doing so [4,5]. The development of encryption is headed for an unavoidable future with endless possibilities. Since hacking is difficult to prevent, we can use encryption techniques to ensure the security of our sensitive data, even if it is compromised [6].
Cryptography basic terms
Plain text: The original message that the person wishes to communicate with the other is defined as plain text. In cryptography the actual message that has to be send to the other end is given a special name as plain text.
Ciphertext: The message that cannot be understood by anyone or meaningless message is what we call as cipher text. In cryptography the original message is transformed into non readable message before the transmission of actual message.
Encryption algorithm: It performs various methods, for example, replacement and change on the plaintext to acquire cipher text.
Decryption algorithm: It is the precisely inverse system of encryption strategy. To acquire unique plaintext, it utilizes cipher text and mystery key.
Key
A key is a numeric or alpha numeric text or can be a unique symbol. The key can be used at the time of encryption takes place on the plain text and at the time of decryption takes place on the Cipher text. The selection of key in cryptography is very important since the security of encryption algorithm depends directly on it (Figure 1).
Figure 1. Cryptographic process.
Matrix
A rectangular array of (real or complex) numbers of the form
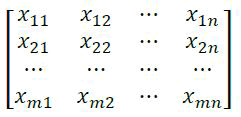
is called a matrix.The numbers x11, …, xmn are called the elements of the matrix. The above matrix has m rows and n columns and is called an (m × n) matrix [7].
Circulant matrix: A circulant matrix is a square matrix in which all row vectors are composed of the same elements and each row vector is rotated one element to the right relative to the preceding row vector. An n × n circulant matrix is defined by n parameters, the elements in the first row, and each subsequent row is a cyclic shift forward of the one above:
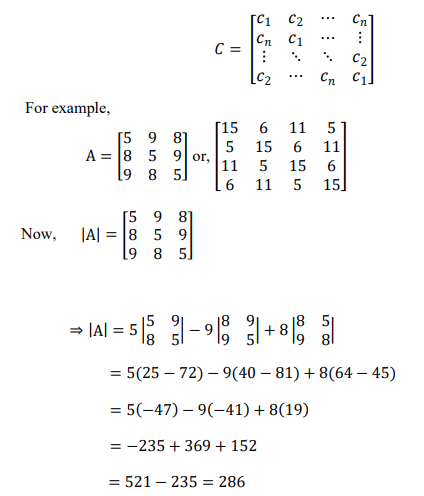
Symmetric matrix: A symmetric matrix is a square matrix that is equal to its transpose. i.e., A=AT . For example,
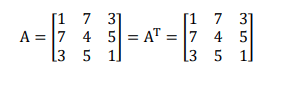
Skew-symmetric matrix: A skew-symmetric matrix is a square matrix whose transpose equals to its negative i.e., A=-AT . For example,
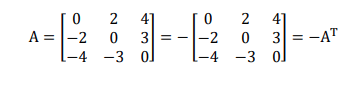
Existing Hill Cipher
The Hill Cipher was invented by Lester S. Hill in 1929. Unlike the others though it is extendable to work on different sized blocks of letters. So, technically it is a poly-graphic substitution Cipher, as it can work on digraphs, trigraphs or theoretically any sized blocks. The Hill Cipher uses an area of mathematics called Linear Algebra. It was the first Cipher that was able to operate on 3 symbols at once.
Method to encrypt using Hill Cipher: To encrypt a message using the Hill Cipher we must first turn our keyword into a key matrix. We also turn the plaintext into digraphs or trigraphs and each of these into a column vector. We then perform matrix multiplication modulo the length of the alphabet (i.e., 26) on each vector. These vectors are then converted back into letters to produce the Cipher text. The plaintext is transformed into by the following procedure:
Step 1. Choose a 3 × 3 matrix with integer values.

Step 2. Group successive plaintext tellers into triples, adding an arbitrary “dummy” letter to fill out the last pair if the plaintext has an odd number of letters and replace each plaintext letter by its numerical value. The numerical value of the alphabet is shown in the below table:
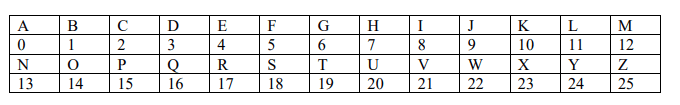
Step 3. Successively convert each plaintext triple P1P2P3 into a column vector.
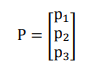
And form the product AP we will call P a plaintext vector and AP the corresponding cipher text vector.
Step 4. Convert each cipher text vector into its alphabetic equivalent.
Proposed Hill Cipher
Step 1. Firstly, convert the message into a block and each blocks contain 4 alphabets. Choose a 4 × 4 matrix with integer values.

Step 2. Select a 4 × 4 key matrix and convert the plaintext vector into a numerical integer value.
Step 3. Successively convert each plaintext P1P2P3P4 into a column vector.
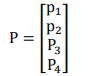
And form the product AP we will call P a plaintext vector and AP the corresponding cipher text vector.
Step 4. Convert each Cipher text vector into its alphabetic equivalent.
Example of hill cipher encryption using 4 × 4 key matrix
Step 1: Encryption.
Message: APPLIED MATHEMATICS Key
Matrix: K =
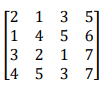
Step 2: Encryption
Message: APPLIED MATHEMATICS
Assign: Numerical value of the alphabet and convert the message in block with 4 alphabets in each block.
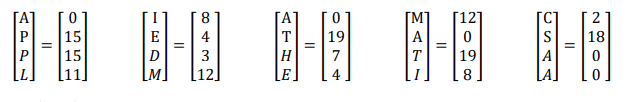
Step 3: Encryption
Message: APPLIED MATHEMATICS
Cipher text = (K × Plaintext) Mod 26
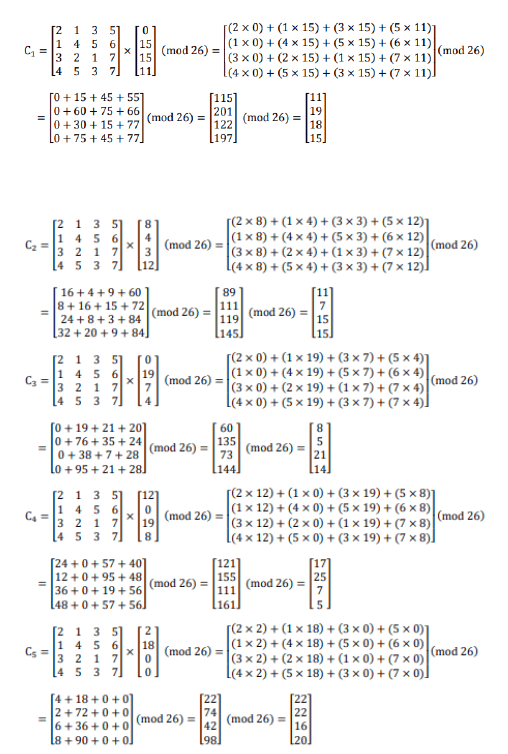
Step 4: Encryption
Message: APPLIED MATHEMATICS
Convert each cipher text vector into its alphabetic equivalent.
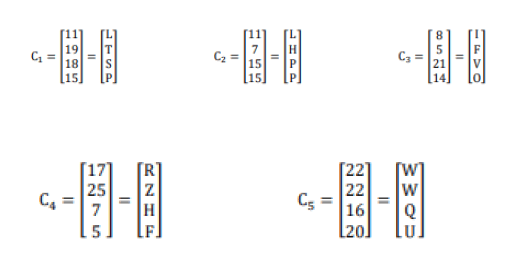
APPLIED MATHEMATICS=LTSPLHP PIFVORZHFWWQU
Example of Hill Cipher decryption using 4 × 4 key matrix
Step 1: Decryption.
Ciphertext: LTSPLHP PIFVORZHFWWQU Key matrix: K=
determinant of key |K| =
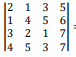
= 126 (mod26) = 22 |K|−1 = (22)−1 mod 26=16 Transpose of key KT=
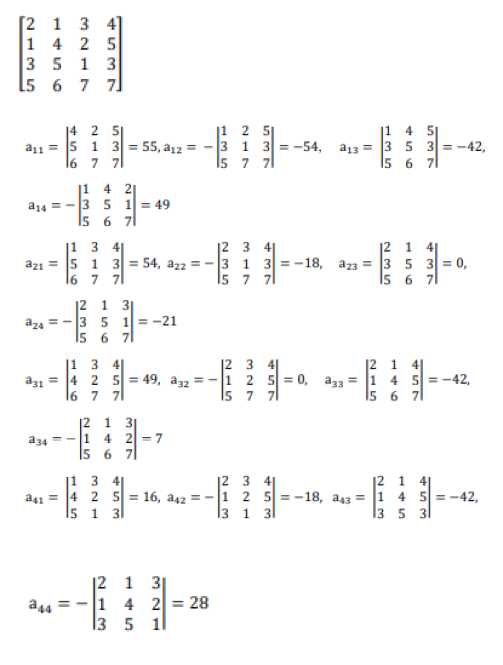
Cofactor matrix of transpose of key
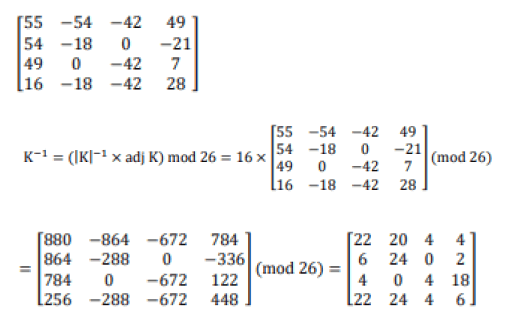
Step2: Decryption
Ciphertext: LTSPLHP PIFVORZHFWWQU
Assign: Numerical value of the alphabet and convert the Cipher text in block with 4 alphabets in each block.
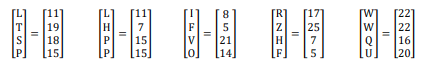
Step 3: Decryption
Ciphertext: LTSPLHP PIFVORZHFWWQU Plain text=(K−1 × Cipher text) Mod 26
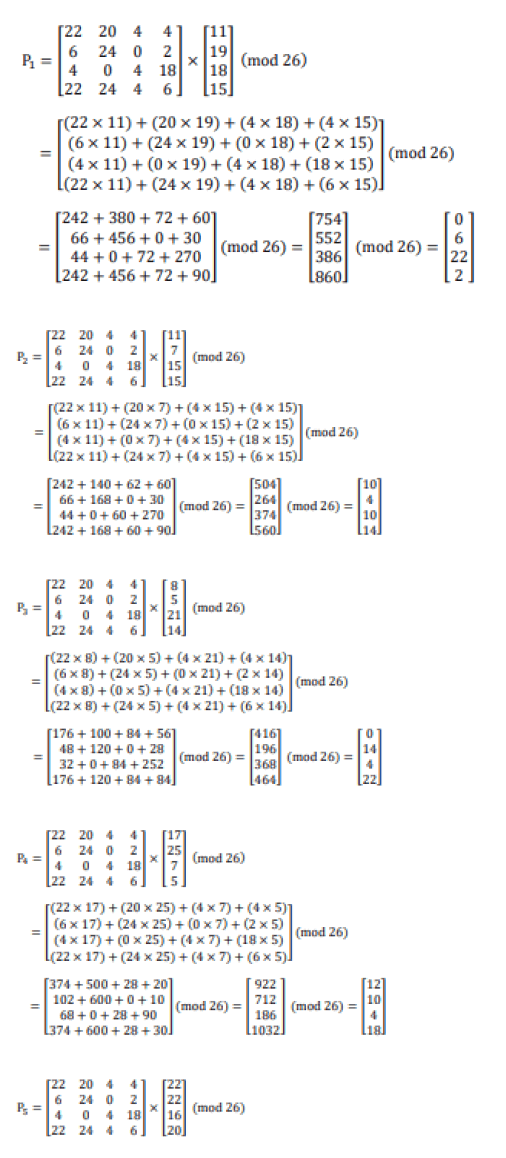
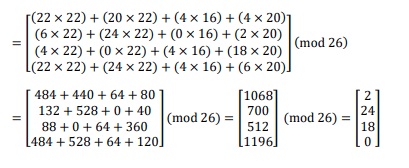
Step 4: Decryption
Ciphertext: LTSPLHP PIFVORZHFWWQU
Convert each plain text vector into its alphabetic equivalent.
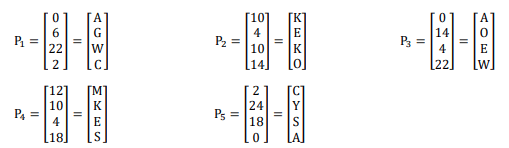
LTSPLHP PIFVORZHFWWQU = AGWCKEK OAOEWMKESCYSA
Output of existing Hill Cipher algorithm using 3 × 3 key matrix
Using MATLAB code, we input different message with the key matrix 3 × 3 then find the output of execution time of encrypt and decrypt message.

Table of existing Hill Cipher using 3 × 3 key matrix input data and corresponding time
We have used the message linear, algebra, calculus, astronomy, technology, integration, cryptography, steganography, aeromechanical and differentiation in the input of the above code of Hill Cipher algorithm using 3 × 3 key matrix and got the execution time of encryption and decryption of respective messages. We have used messages of different length where message length of linear, algebra, calculus, astronomy, technology, integration, cryptography, steganography, aeromechanical and differentiation are respectively 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14 and 15 (Table 1).
| SI. no. | Message | Number of letters | Execution time (in second) |
| 1 | Linear | 6 | 6.212 |
| 2 | Algebra | 7 | 8.098 |
| 3 | Calculus | 8 | 14.039 |
| 4 | Astronomy | 9 | 16.752 |
| 5 | Technology | 10 | 18.415 |
| 6 | Integration | 11 | 21.542 |
| 7 | Cryptography | 12 | 22.969 |
| 8 | Steganography | 13 | 23.38 |
| 9 | Aeromechanical | 14 | 29.447 |
| 10 | Differentiation | 15 | 34.003 |
Table 1. Execution time using 3 × 3 key matrix.
Graphical representation of existing Hill Cipher using 3 × 3 key matrix
Considering execution time as y-axis and message length as xaxis, we represent the above data of Hill Cipher using 3 × 3 key matrix graphically as follows in Figure 2.
Figure 2. Hill Cipher using 3 × 3 key matrix.
Output of proposed Hill Cipher algorithm using 4 × 4 key matrix
Using MATLAB code, we input different message with the key matrix 4 × 4 then find the output of execution time of encrypt and decrypt message.
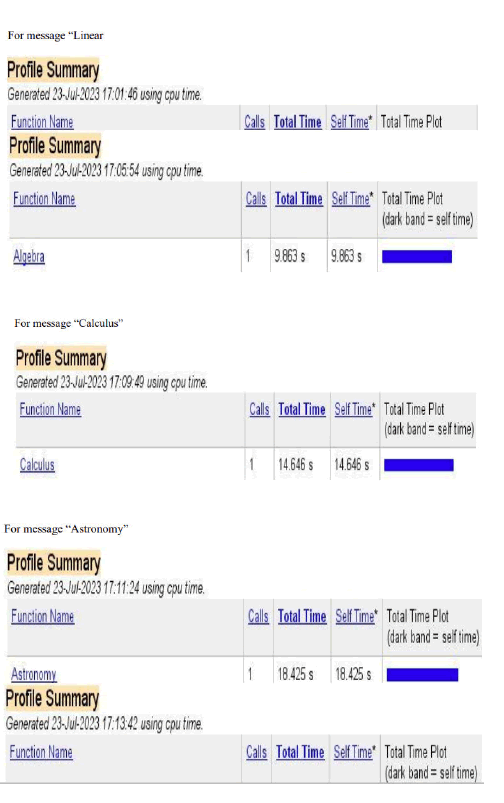
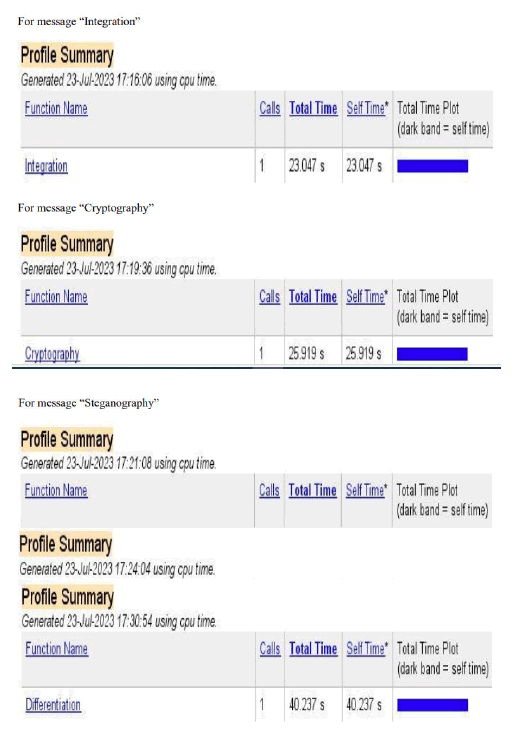
Table of proposed Hill Cipher using 4 × 4 key matrix input data and corresponding time
We have used the message linear, algebra, calculus, astronomy, technology, integration, cryptography, steganography, aeromechanical and differentiation in the input of the above code of hill cipher algorithm using 4 × 4 key matrix and got the execution time of encryption and decryption of respective messages. We have used messages of different length where message length of linear, algebra, calculus, astronomy, technology, integration, cryptography, steganography, aeromechanical and differentiation are respectively 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14 and 15 (Table 2).
| SI. no. | Message | Number of letters | Execution time (in second) |
| 1 | Linear | 6 | 6.88 |
| 2 | Algebra | 7 | 9.863 |
| 3 | Calculus | 8 | 14.646 |
| 4 | Astronomy | 9 | 18.425 |
| 5 | Technology | 10 | 20.381 |
| 6 | Integration | 11 | 23.047 |
| 7 | Cryptography | 12 | 25.919 |
| 8 | Steganography | 13 | 27.664 |
| 9 | Aeromechanical | 14 | 33.859 |
| 10 | Differentiation | 15 | 40.237 |
Table 2. Execution time using 4 × 4 key matrix.
Graphical representation of proposed Hill Cipher using 4 × 4 key matrix
Considering execution time as y-axis and message length as xaxis, we represent the above data of Hill Cipher using 4 × 4 key matrix graphically as follows in Figures 3 and 4.
Figure 3. Hill Cipher using 4 × 4 key.
Figure 4. Comparison of Hill Cipher using 3 × 3 and 4 × 4 key matrix.
By analyzing above output of the code and the graph of the both algorithms we conclude that proposed Hill cipher algorithm using 4 × 4 key matrix is more complicated and time consuming than the existing Hill Cipher algorithm using 3 × 3 key matrix which makes it more secure than the existing Hill Cipher algorithm.
In this paper, we have proposed the Hill Cipher algorithm using 4 × 4 key matrix as against the traditional Hill Cipher algorithm of 3 × 3 key matrix. The important aspect of Hill Cipher cryptography is the selection of key matrix and which blocks of key matrix use to generate matrix multiplication. In this technique symmetric key use for both encryption and decryption. The security of Hill cipher cryptosystem is based on the hope that the encryption function is one way and so it is computationally infeasible for an intruder to decrypt a cipher text. As 4 × 4 key matrix is used here, the strength of key is dependent on the inverse of 4 × 4 key matrix. The calculation will be complex it will be more difficult to any intruders to find the original message. In this paper, the algorithms are generated using only small numbers of key matrix but large numbers can be implemented using the code of MATLAB language written in result and discuss section. Hence by comparing the time consumed to encrypt and decrypt a message using traditional and enhanced Hill Cipher we can state that the enhanced Hill Cipher is more efficient and reliable and also not easily breakable by the intruders. In future we may improve or enhance the Hill cipher algorithm more by using more than 3 × 3 or 4 × 4 key matrix. This will make the multiplication of n × n matrix more complicated and our message will be much more secured from the intruders, as they will not be able to easily decipher the Cipher text.
We are grateful to the Ministry of Science and Technology, Bangladesh for providing the financial support to work with this article.
Journal of Applied & Computational Mathematics received 1282 citations as per Google Scholar report